Silicon nitrade ceramics help heat dissipation
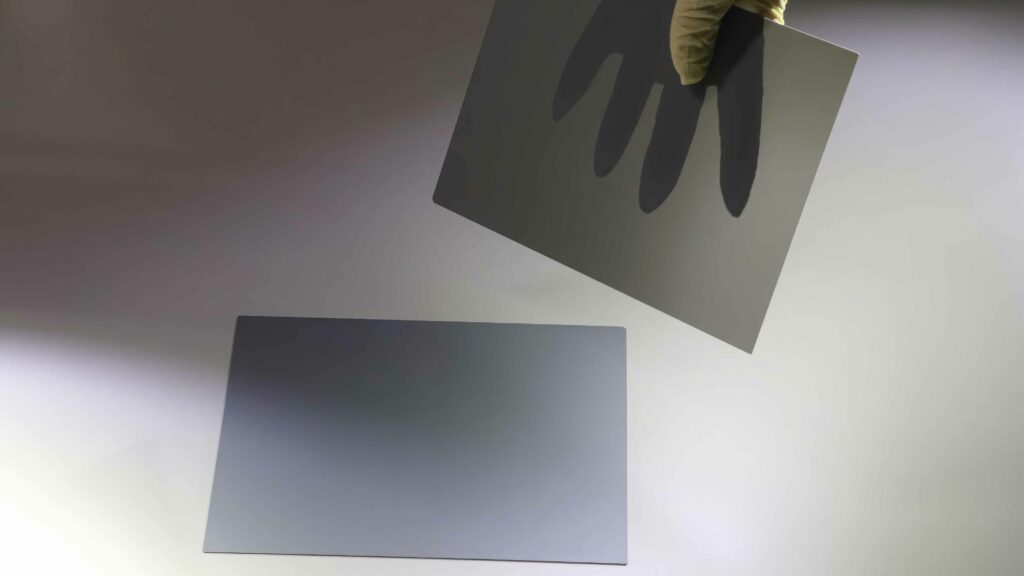

(Image courtesy of NGK Insulators)
The National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) in Japan is working with NGK Insulators to standardise evaluation methods for measuring thermal diffusivity of thin substrates, writes Nick Flaherty.
The work aims to validate methods for evaluating the thermal diffusivity of silicon nitride ceramic substrates used for power semiconductors in e-mobility designs.
Adoption of EVs and hybrid EVs is boosting use of power semiconductor modules in inverters, raising demand for thinner substrates with substantial thermal dissipation performance.
Silicon nitride ceramics play a vital role in active metal brazing (AMB) substrates for power modules for heat dissipation. The thinner the substrate and the higher its thermal diffusivity, the greater the efficiency of the power semiconductor module. But there are no standards for substrates less than 0.5 mm thick.
AMB substrates for power modules consist of a silicon nitride ceramic substrate and two copper plates. The AMB circuit substrates for power semiconductor modules of NGK have proprietary advanced bonding technology to create an extremely thin bonding layer of a few microns or less between the ceramic substrate and copper plates. This greatly reduces thermal resistance and internal strain in the bonding layer, resulting in exceptional thermal dissipation properties.
The research taps into the AIST’s evaluation expertise, along with NGK and its advanced ceramic substrate technology, in an effort to collect data for quantifying the preliminary process, which affects the measurement of thermal diffusivity of substrates.
Click here to read the latest issue of E-Mobility Engineering.
ONLINE PARTNERS