InfiMotion unveils magnesium‑alloy integrated drive system for high‑efficiency EVs
(Image courtesy of InfiMotion)
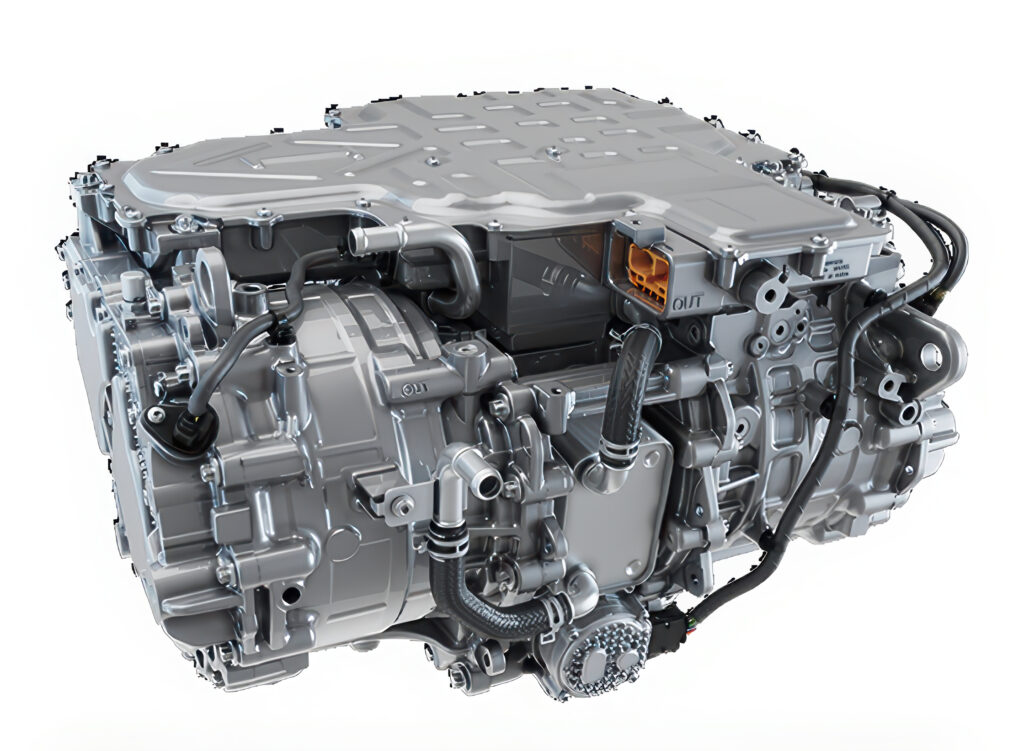
InfiMotion Technology in China has developed a lightweight integrated drive system with a magnesium housing to reduce the weight, writes Nick Flaherty.
The TL300 combines dual motors, dual inverters and a common power control module in a single unit built from a magnesium alloy that reduces the mass of the housing by 25%. This reduces the mass of the overall unit by 10% to 109.5 kg.
The system incorporates a patented 360° bidirectional full-oil cooling architecture for thermal management. This allows the dual 170 kW motors running at 18,000 rpm to provide sub five second 0-100 km/h acceleration times without power derating for over 20 consecutive cycles.
The motor topologies and advanced control algorithms include torque vectoring up to 3400 Nm from each motor with peak system efficiency of 89.5%. The adjustable magnetic field motor features a breakthrough structural design that innovatively integrates auxiliary electric excitation windings.
This design combines the flexibility of magnetic field adjustment from electrically excited synchronous motors with the high-efficiency characteristics of permanent magnet motors. It significantly reduces no-load drag losses and decreases such losses by 1.5% compared with traditional permanent magnet synchronous motors under peak power conditions. This effectively optimises the overall vehicle electrical consumption performance, providing a substantial improvement in the driving range for EVs.
The power control module uses an intelligent hybrid parallel configuration of SiC and silicon IGBT power semiconductor devices. This dynamically allocates semiconductor usage based on operational demands, thereby maximising system efficiency. This is a module architecture that can be adapted for a range of vehicle platforms and operating profiles including off-road designs up to 800 V.
The motor uses a W-pin hairpin topology that avoids the need for end weld points and reduces the end height, significantly reducing the axial space. The stator closed slot design effectively suppresses torque ripple, improving the noise, vibration and harshness (NVH) performance. It can use the crossflow oil cooling system, which efficiently cools the winding ends without an oil ring, resolving the problem of motor temperature rise. This provides a more compact, reduced-noise and reliable solution for electric drive systems.
Click here to read the latest issue of E-Mobility Engineering.
ONLINE PARTNERS